|technology, knowledgehub
What Are Centralized, Decentralized and Distributed Systems?

Centralization, decentralization, and distribution shape the design and operation of technology systems, but what do centralized, decentralized, and distributed systems really mean?
While commonly associated with blockchain and cryptocurrency, these principles apply across industries and influence how organizations manage resources, share information, and empower users.
Let's explore the differences between centralized, decentralized, and distributed systems and how each approach addresses challenges around fault tolerance, security, and scalability.
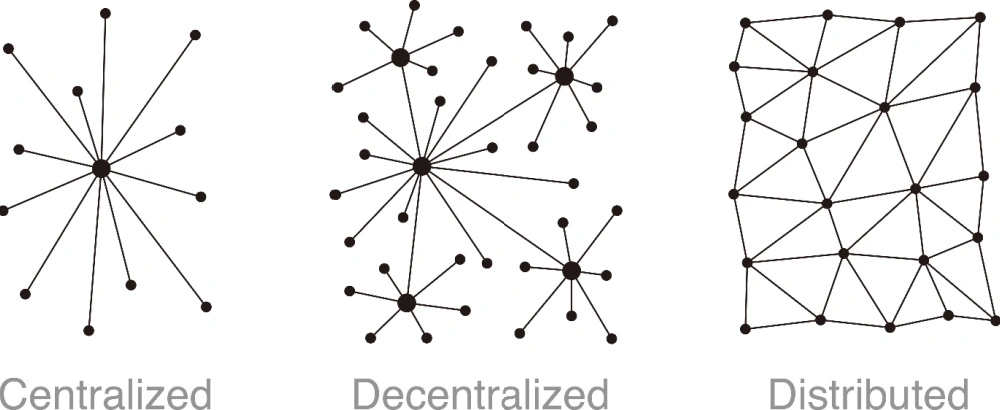
Control and access to resources within a system are distributed according to these classifications. Let’s start with a centralized system. A single authority oversees and manages data, as well as coordinates access in a centralized system.
Decentralized and distributed systems, however, spread control across multiple independent actors or locations. But there are important nuances to each model.
Centralized systems, like traditional banks, consolidate power in one place for simplified coordination. However, if that central point fails or is compromised, it creates vulnerabilities.
Decentralized systems remedy this by dispersing control while retaining some coordination, much like a franchised business. On the other hand, distributed systems eliminate centralization altogether by sharing control across all participants, akin to peer-to-peer file-sharing networks.
The significance of different systems
Organizations often prioritize security, scalability, and flexibility when determining the type of system to use. Centralized systems are generally easier to manage but introduce single points of failure.
Decentralized networks aim to avoid these weaknesses at the cost of reduced efficiency. Meanwhile, distributed systems seek to balance control with the benefits of dispersing resources.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of decentralization?
Decentralization provides some compelling benefits. Without centralized control or infrastructure, decentralized networks can be highly resilient.
The loss of any single node won't disrupt the whole system. This architecture also makes censorship and tampering very difficult, as there is no one entity to target. However, decentralization introduces certain trade-offs.
Coordinating across independent blockchain nodes can reduce efficiency. Reaching consensus takes more communication and overhead compared to simple commands from a central point.
Directly interacting with decentralized protocols instead of relying on centralized services may also reduce usability. The lack of centralized governance brings additional challenges around standards and upgrades.
What are the pros and cons of centralized systems?
Centralization provides an intuitively simple model that is easy to set up and manage. A centralized authority in full control optimizes system performance.
Upgrades and changes can roll out quickly from the top down. Centralized platforms also tend to offer polished consumer experiences focused on ease-of-use.
On the flip side, centralized points of control introduce single points of failure. Compromising or taking the central server or authority offline results in the entire system suffering.
This model lacks resilience and invites more risk of censorship or tampering from governments, hackers, or other bad actors. Over-reliance on third parties for control and infrastructure can also reduce user privacy and autonomy in the long term.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a distributed system?
Distributed systems aim to balance the benefits of centralization with the resilience of decentralization. By dispersing infrastructure across multiple nodes, distributed networks gain fault tolerance without depending on a single point of failure.
This provides better uptime guarantees and security compared to centralized architectures. However, distributed systems bring some downsides to both centralization and decentralization. Coordination across blockchain nodes adds complexity versus pure centralization.
And nodes may still report to a central authority, reducing the full autonomy of pure decentralization. Furthermore, nodes that store redundant information in distributed approaches also encounter challenges regarding data consistency, as they must synchronize this information.
What is centralized and decentralized in a distributed system?
Within distributed systems, individual nodes can still take on centralized or decentralized roles. Independent nodes in a distributed database system handle data storage and processing.
But a coordination mechanism like blockchain technology maintains a shared ledger in a decentralized manner without centralized governance. Other systems blend centralized and decentralized components.
Cryptobunq, for example, offers custody and wallet, and crypto payment services through a centralized cloud platform but also supports decentralized networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. This flexibility of CBQ, a one-stop-shop crypto service provider, allows for maximizing the benefits of each approach.
Is blockchain decentralized or distributed?
Blockchain technology is both decentralized and distributed. At its core, blockchain consists of distributed nodes running identical copies of a transaction ledger using a distributed consensus mechanism like proof-of-work. This distributed architecture ensures no single entity controls the ledger.
Blockchains are also decentralized since there is no centralized authority. Instead, network participants validate blockchain transactions and updates through economic incentives.
For example, systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum allow anyone to participate without permission. This improves resilience by avoiding centralized control or governance and providing more freedom for the users.
Is cryptocurrency a decentralized system?
Most major cryptocurrencies operate as decentralized systems. Bitcoin, for example, functions through distributed consensus across thousands of nodes worldwide without centralized governance or control over the Bitcoin protocol or ledger. Users can participate directly on the network without intermediaries.
However, varying degrees of centralization exist in some cryptocurrencies and stablecoins. While built on open blockchain networks, assets like EURK maintain reserves in regulated banks and face legal or operational centralization.
Others operate through centralized exchanges that act as gatekeepers. The degree of decentralization depends on the network structure and governance model.
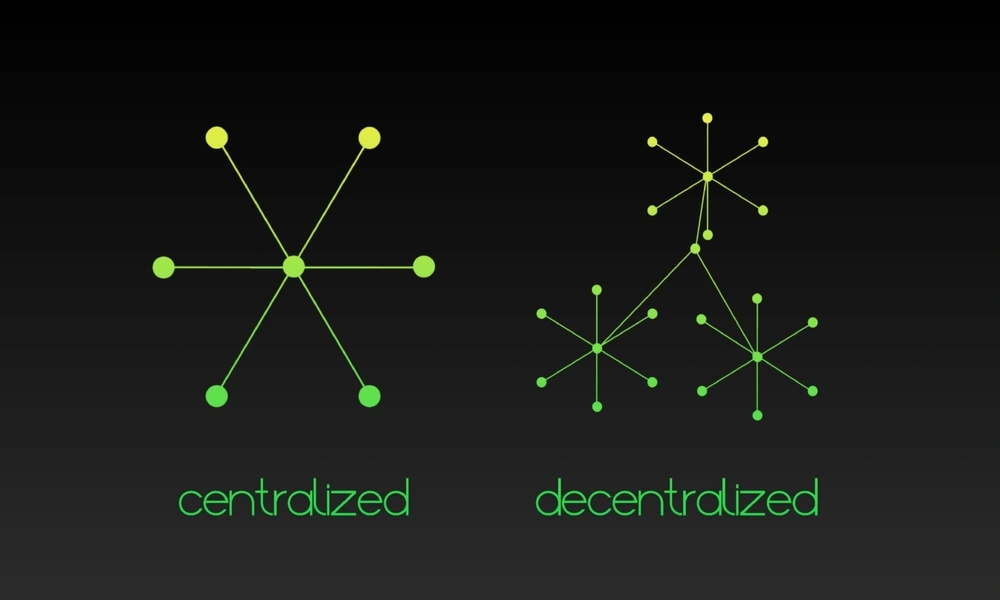
What is the difference between decentralized and centralized systems?
Distributed control differs between decentralized and centralized systems. Centralized systems consolidate authority within a single entity, while decentralized networks distribute it across multiple equal participants.
Centralization provides simplicity but introduces vulnerabilities at single points of failure. Decentralization improves resilience but adds complexity to coordination. Performance characteristics also differ, with centralized tending to be faster but decentralized being more resistant to censorship.
Centralized systems are best for consistency and ease of management. Decentralized networks promote open access and resilience at the cost of more complex coordination challenges. Therefore, the optimal choice depends on specific use cases and design priorities.
What is the difference between decentralized and distributed systems?
Both decentralized and distributed systems disperse elements of control across multiple nodes. However, in a decentralized system, nodes are equal participants who share authority over the network. Distributed systems maintain a division of labor between nodes through coordination mechanisms.
For example, in Bitcoin, all full nodes validate transactions equally as peers. But in a distributed database, nodes specialize as clients, servers, or caches and coordinate to reach consensus.
Decentralization focuses more on the political dispersion of control, while distribution emphasizes the operational diffusion of workloads. Network participants partition control, data, and tasks to create the distinction.
In practice, many systems blend these concepts, such as with blockchain technology that maintains a distributed transaction ledger through decentralized consensus protocols.
What is the difference between centralization, decentralization, and distribution?
Centralization refers to consolidating control within a single authority, while decentralization distributes it across equal peers. Distribution involves dispersing workloads, resources, or data processing responsibilities across interconnected nodes.
Centralized systems rely on a central point of control but are vulnerable to failure. Decentralized networks avoid central points but add coordination overhead. Distributed systems balance these by dispersing work through autonomous nodes that coordinate roles.
Furthermore, centralization focuses on governance, decentralization on political structures, and distribution on operational responsibilities. These are the main differences between centralization, decentralization, and distribution.
However, real-world systems often blend these concepts. For example, distributed databases maintain decentralized consensus using blockchain technology. In the end, the optimal approach depends on specific technical and organizational priorities.
The bottom line
In today's digital landscape, the choice between centralized, decentralized, and distributed systems architectures impacts resilience, governance, coordination, and more.
Emerging technologies increasingly leverage decentralization and distribution to improve open access, censorship resistance, and single-point failure risks. Understanding these fundamental concepts is crucial as new innovations reshape how networks are built.
Whether it's evaluating new payment rails, data storage solutions, or organizational structures, the tradeoffs between these approaches must be carefully considered based on unique needs, priorities, and threat models.
As networks scale to unprecedented levels, balancing these design philosophies will remain an ongoing challenge. Cryptobunq is a crypto-friendly digital bank offering various services in crypto and blockchain for you to overcome the challenges of cryptocurrency.
Cryptobunq offers node as a service, exchange APIs, tokenization, batch payments, and many more crypto solutions as a one-stop shop crypto service provider. Integrate with Cryptobunq and start using the benefits of cryptocurrency and blockchain. Explore our case studies and contact us today!